Price Channel
A price channel is a continuation pattern that slopes up or down and is bound by an upper and lower trend line. The upper trend line marks resistance and the lower trend line marks support. Price channels with negative slopes (down) are considered bearish and those with positive slopes (up) bullish. For explanatory purposes, a “bullish price channel” will refer to a channel with positive slope and a “bearish price channel” will refer to a channel with negative slope.
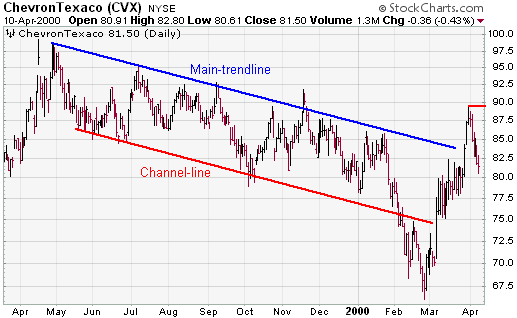
- Main Trend Line: It takes at least two points to draw the main trend line. This line sets the tone for the trend and the slope. For a bullish price channel, the main trend line extends up and at least two reaction lows are required to draw it. For a bearish price channel, the main trend line extends down and at least two reaction highs are required to draw it.
- Channel Line: The line drawn parallel to the main trend line is called the channel line. Ideally, the channel line will be based off of two reaction highs or reaction lows. However, after the main trend line has been established, some analysts draw the parallel channel line using only one reaction high or low. The channel line marks support in a bearish price channel and resistance in a bullish price channel.
- Bullish Price Channel: As long as prices advance and trade within the channel, the trend is considered bullish. The first warning of a trend change occurs when prices fall short of channel line resistance. A subsequent break below main trend line support would provide further indication of a trend change. A break above channel line resistance would be bullish and indicate an acceleration of the advance.
- Bearish Price Channel: As long as prices decline and trade within the channel, the trend is considered bearish. The first warning of a trend change occurs when prices fail to reach channel line support. A subsequent break above main trend line resistance would provide further indication of a trend change. A break below channel line support would be bearish and indicate an acceleration of the decline.
- Scaling: Even though it is a matter of personal preference, trend lines seem to match reaction highs and lows best when semi-log scales are used. Semi-log scales reflect price movements in percentage terms. A move from 50 to 100 will appear the same distance as a move from 100 to 200.
In a bullish price channel, some traders look to buy when prices reach main trend line support. Conversely, some traders look to sell (or short) when prices reach main trend line resistance in a bearish price channel. As with most price patterns, other aspects of technical analysis should be used to confirm signals.
Because technical analysis is just as much art as it is science, there is room for flexibility. Even though exact trend line touches are ideal, it is up to each individual to judge the relevance and placement of both the main trend line and the channel line. By that same token, a channel line that is exactly parallel to the main trend line is ideal.
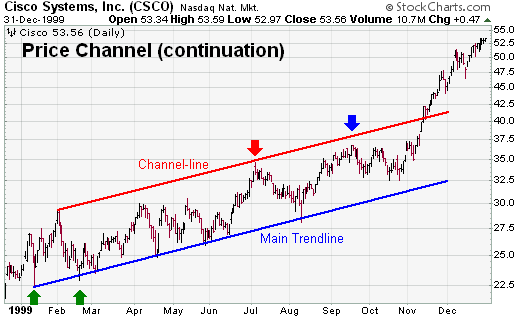
CSCO provides an example of an 11-month bullish price channel that developed in 1999.
- Main Trend Line: The January, February, and March reaction lows formed the beginning of the main trend line. Subsequent lows in April, May, and August confirmed the main trend line.
- Channel Line: Once the main trend line was in place, the channel line beginning from the January high was drawn. A visual assessment reveals that these trend lines look parallel. More precise analysts may want to test the slope of each line, but a visual inspection is usually enough to ensure the “essence” of the pattern.
- Bullish Price Channel: Subsequent touches along the main trend line offered good buying opportunities in mid-April, late May and mid-August.
- The stock did not reach channel line resistance until July (red arrow) and this marked a significant reaction high.
- The September high (blue arrow) fell short of channel line resistance, but only by a small margin that was probably insignificant.
- The break above channel line resistance in Dec-99 marked an acceleration of the advance. Some analysts might consider the stock overextended after this move, but the advance was powerful and the trend never turned bearish. Price channels will not last forever, but the underlying trend remains in place until proved otherwise.